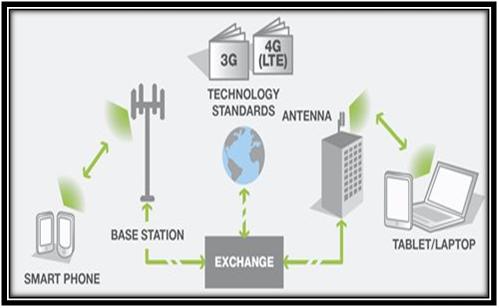
LTE Omnet (Long Term Evolution) the successor to UMTS and also HSPA. LTE Omnet simulation framework is now being deploy mainly due to high speed cellular service. In LTE Advance method able also to operate more efficiently with respect to the use of spectrum, and also to provide the much higher data rates that are being required.
Parameters considered in LTE-Omnet Project
- Access schemes like OFDMA or SC-FDMA.
- Peak downlink speed.
- Modulation types supported.
- Latency.
- Data type.
- Spectral efficiency.
- Duplex schemes.
- Peak uplink speeds.
- Channel bandwidth.
- Mobility etc.
Main/important LTE technologies:
- System architecture evolution.
- Orthogonal frequency division multiplex.
- Also Multiple input multiple output.
Download Sample LTE-Omnet Code.
//This is the sample code for LTE.
//package lte.simulations.demo;
import inet.networklayer.autorouting.ipv4.IPv4NetworkConfigurator;
import inet.networklayer.ipv4.RoutingTableRecorder;
import inet.nodes.ethernet.Eth10M;
import inet.nodes.inet.Router;
import inet.nodes.inet.StandardHost;
import inet.world.radio.ChannelControl;
import lte.corenetwork.binder.LteBinder;
import lte.corenetwork.nodes.Ue;
import lte.corenetwork.nodes.eNodeB;
network MultiCell
{
parameters:
@display("i=block/network2;bgb=991,558;bgi=background/budapest");
submodules:
channelControl: ChannelControl {
@display("p=50,25;is=s");
}
routingRecorder: RoutingTableRecorder {
@display("p=50,75;is=s");
}
ipConfigurator: IPv4NetworkConfigurator {
@display("p=50,125");
config = xmldoc("multi.xml");
dumpTopology = true;
}
binder: LteBinder {
@display("p=50,175;is=s");
}
server: StandardHost {
@display("p=212,118;is=n;i=device/server");
}
router1: Router {
@display("p=321,136;i=device/smallrouter");
}
router2: Router {
@display("p=614,116;i=device/smallrouter");
}
eNodeB1: eNodeB {
@display("p=391,259;is=vl");
}
eNodeB2: eNodeB {
@display("p=760,125;is=vl");
}
ue11: Ue {
@display("p=211,271");
}
ue12: Ue {
@display("p=537,424");
}
ue21: Ue {
@display("p=805,484");
}
ue22: Ue {
@display("p=950,271");
}
connections:
server.pppg++ <--> Eth10M <--> router1.pppg++;
router1.pppg++ <--> Eth10M <--> router2.pppg++;
router1.pppg++ <--> Eth10M <--> eNodeB1.ppp;
router2.pppg++ <--> Eth10M <--> eNodeB2.ppp;
}